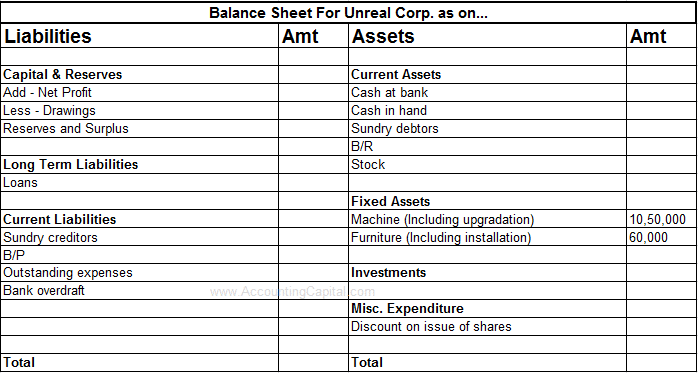
The two examples of deferred revenue expenditure and their treatment in final accounts are as explained below. The reason for deferring recognition of the cost as an expense is. Thus only a part of such expenditure is taken to Profit and Loss accounts every year the unwritten-off portion is allowed to stand on the assets side of the balance sheet. An exception is the costs of issuing long-term bonds. The deferred expenses that will not become expenses within one year of the date of the balance sheet will be reported in the long-term asset section of the balance sheet under the classification of other assets. Deferred Revenue Expenditure is an expenditure which is revenue in nature and incurred during an accounting period however related benefits are to be derived in multiple future accounting periods. Deferred revenue which is also referred to as unearned revenue is listed as a liability on the balance sheet because under accrual accounting the revenue recognition process has not been. In its most raw form the entry is debit cash credit Deferred Revenue balance sheet - liabilities. Definition of Deferred Expense. Deferred revenue expenditure is that expenditure for which payments will be made immediately in the year occurred but wont be accounted full in the books of accounts.
The two examples of deferred revenue expenditure and their treatment in final accounts are as explained below. An exception is the costs of issuing long-term bonds. What is a deferred expense. Thus only a part of such expenditure is taken to Profit and Loss accounts every year the unwritten-off portion is allowed to stand on the assets side of the balance sheet. All assets are capitalized however the cost is eventually matched with its future revenue till then it is only a deferred expense waiting to be expensed. Deferred revenue is the amount of income earned by the company for the goods sold or the services however the product or service delivery is still pending and examples include like advance premium received by the insurance companies for prepaid insurance policies etc. The deferred revenue expenditure is spread over the number of years for which the benefits is likely to last. Deferred revenue is often mixed with accrued expenses since both share some characteristics. Thus it shows the balance of the benefit that it will reap in future on the Assets of the Balance Sheet. The difference between the two terms is that deferred revenue refers to goods or services a company owes to its customers.
Sometimes some expenditure is of revenue nature but its benefit likely to be derived over a number of years. Deferred revenue expenditure is that expenditure for which payments will be made immediately in the year occurred but wont be accounted full in the books of accounts. It is shown as an asset in the companys final accounts. These expenses are unusually large in amount and essentially the benefits are not consumed within the same accounting period. Deferred Revenue expenditure are usually large in amount and benefits are not consumed within the same accounting period. You will record deferred revenue on your business balance sheet as a liability not an asset. The reason for deferring recognition of the cost as an expense is. In its most raw form the entry is debit cash credit Deferred Revenue balance sheet - liabilities. Deferred revenue is the amount of income earned by the company for the goods sold or the services however the product or service delivery is still pending and examples include like advance premium received by the insurance companies for prepaid insurance policies etc. Deferred Revenue arises when you receive revenue that you have not yet earned but obviously expect to earn at a future date.
All assets are capitalized however the cost is eventually matched with its future revenue till then it is only a deferred expense waiting to be expensed. Example Deferred Revenue Expenditure Net Book Value of an asset on the balance sheet is its unexpired cost. For example both are shown on a businesss balance sheet as current liabilities. These expenses are unusually large in amount and essentially the benefits are not consumed within the same accounting period. It is when the firm derives a portion of the benefit in the current accounting year and will reap the balance in the future years. Deferred Revenue is not expenditure so your question needs work. It is shown as an asset in the companys final accounts. Deferred revenue is often mixed with accrued expenses since both share some characteristics. Thus it shows the balance of the benefit that it will reap in future on the Assets of the Balance Sheet. The reason for deferring recognition of the cost as an expense is.
Deferred revenue is a liability on a companys balance sheet that represents a prepayment by its customers for goods or services that have yet to be delivered. The two examples of deferred revenue expenditure and their treatment in final accounts are as explained below. Deferred revenue expenditure is that expenditure for which payments will be made immediately in the year occurred but wont be accounted full in the books of accounts. Thus only a part of such expenditure is taken to Profit and Loss accounts every year the unwritten-off portion is allowed to stand on the assets side of the balance sheet. Sometimes some expenditure is of revenue nature but its benefit likely to be derived over a number of years. These expenses are unusually large in amount and essentially the benefits are not consumed within the same accounting period. The deferred revenue expenditure is spread over the number of years for which the benefits is likely to last. Deferred revenue is often mixed with accrued expenses since both share some characteristics. The difference between the two terms is that deferred revenue refers to goods or services a company owes to its customers. An exception is the costs of issuing long-term bonds.